SCHOOL WHICH EXPLORES EFFECTIVE LEARNING METHODS
May 3, 2023
List of Neighboring Countries of India
June 22, 2023Top 12 Major And Longest Rivers in India
India is known to be the land of rivers, which is justified because our country has so many rivers. Our country’s economic development is majorly influenced by these rivers. These rivers have been categorized into two namely Himalayan Rivers and Peninsular Rivers.
The country has over 200 rivers and these rivers not only include the long rivers, but also the tributaries. Most of these rivers originate from Karakoram, Aravali, and the Himalayas. And most of these are situated in the western part of India.
At JBM Smart Start- the best school in Greater Noida West, our educational program includes comprehensive lessons about rivers. Through interactive learning students gain a deep appreciation for the vital role of rivers in our ecosystems, cultures, and the environment, fostering environmental stewardship.
In this article, we have talked about the 12 longest rivers in India.
Importance of Rivers
Rivers are the major source of carrying water and nutrients to all areas. They are an important part of the water cycle. Rivers are also a major source of food and habitat for many organisms. Apart from this, water is a major source of transport, farming, energy, and many other things.
Above all, rivers are the only source for us to source drinking water. Approximately 96% of the water body has saline water and it is not suitable for humans to consume. Thus, rivers are the source that we majorly rely on.
1. Agriculture: Rivers help to remove extra precipitation, avoiding water logging and floods. Rivers are used for irrigation and extensively help in agriculture in many ways.
2. Transportation: River allows transportation routes that ease human travel and even import-export of goods.
3. Economy: Water acts as a main source of income for many people around the world. Modern agriculture also relies on rivers, which contribute majorly to the country’s economy.
4. Source of energy: Rivers generate energy as they carry a lot of currents. This energy can be used by machines to generate electricity.
Also Read: List of Neighboring Countries of India
Let us look at the vital status of our existing rivers through various cities:
12 Longest Rivers in India
| River Name | Total Length | Mouth | Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Ganga River | 2,525 KM | Ganga Delta | Gangotri Glacier |
| 2. Indus River | 3,180 KM | Arabian Sea, Rann of Katch, Nal Sarovar Bird Sanctuary | Gar River, Sengge Zangbo, Tibetan, Plateau |
| 3. Brahmaputra River | 2,900 KM | Ganges, Bay of Bengal | Himalayas |
| 4. Yamuna River | 1,376 KM | Triveni Sangam | Yamunotri, Champasar Glacier |
| 5. Narmada River | 1,312 KM | Arabian Sea, Gulf of Khambhat | Amarkantak |
| 6. Krishna River | 1,400 KM | Hamsalade vi, Bay of Bengal | Mahabaleshwar |
| 7. Sutlej River | 1,450 KM | Arabian Sea | Lake Rakshastal in Tibet |
| 8. Godavari River | 1,465 KM | Bay of Bengal | Trimbakeshwar |
| 9. Kaveri River | 800 KM | Bay of Bengal | Tala Kaveri, |
| 10. Mahanadi River | 900KM | False Point | Sihawa |
| 11. Tapti River | 724 KM | Gulf of Khambhat, Arabian Sea | Satpura Range |
| 12. Chambal River | 1024 KM | Yamuna | Janapav |
In India, rivers were traditionally worshipped, rather than just being a source of water. Multiple rivers are flowing throughout the country.
Here are the top 12 longest rivers in India and everything that you need to know about them.
1. Ganga River
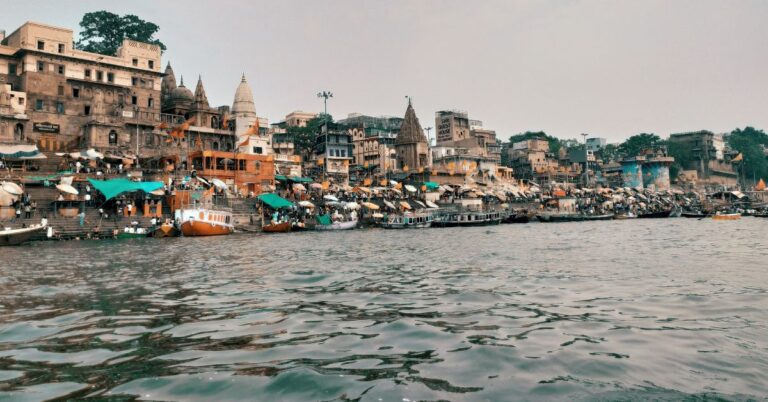

The Ganges is one of the longest rivers in India and is the third-largest one on the globe. It is worshiped as “Goddess Ganga” and is considered sacred with a special place in Hindu Mythology. It provides a lifeline to millions of people who rely on it for their daily needs.
Ganga is 2,525 km long and originates from the western Himalayas in Uttarakhand from Gangotri Glacier. The river flows through the nation and empties into the Bay of Bengal.
It flows south and north from the North Indian River Plain. It receives the right bank tributary Yamuna and the left bank tributaries from Nepal. Some of these tributaries are Son, Chambal, Kosi, and Ghaghra.
2. Godavari River
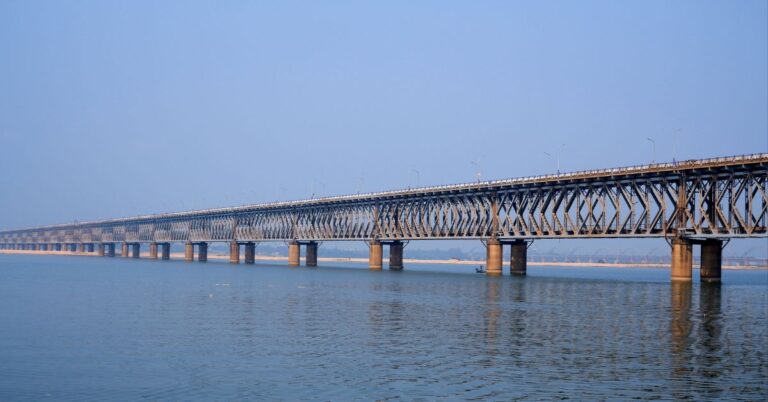

The Godavari is also known as “Dakshin Ganga” or “Ganges of South” because of its long course. It is the second-longest river in India.
It is 1465 km long and it rises from the Western Ghats in Trimbakeshwar in Nashik, Maharashtra, and falls into the Bay of Bengal. The river flows through the states of Maharashtra, Andhra Pradesh, Telangana, and Chattisgarh. The main tributaries of Godavari are Purna, Manjra, Pravara, Wardha, and Wainganga.
Also Read: 50+ Vegetable Names in English
3. Krishna River

Krishna River is the third-longest river in India. And also the second-largest east-flowing river of the peninsular region. It flows through Karnataka, Andhra Pradesh, and Telangana.
The river rises from the Western Ghats near Jor village in Maharashtra. Its final point of destination is the Bay of Bengal. Krishna River is 1400 km long and the third longest river in India considering the distance it covers within the country.
The main tributaries of the Krishna River are Panchganga, Bhima, Dudhaganga, Tungabhadra, and Ghataprabha
4. Yamuna River

The Yamuna is a major river in Northern India. It is the second-longest tributary of the Ganga by discharge and also the longest tributary in India. According to Hindu mythology, Yamuna is considered to be the sister of Yama, the God of Death and the daughter of the Sun God.
River Yamuna originates from the Yamunotri glacier at the Banderpoonch peak in Uttarakhand. It is the longest tributary of the Ganges. Yamuna is 1376 km long. It meets Ganga at Triveni Sangam.
Its tributaries are Hindon, Giri, Rishiganga, Sharda, Sasur, Hanuman Ganga, Betwa, Chambal, Sindh, Ken, and Tons. It merges after Kalsi in proximity to Dehradun.
Also Read: List Of Young Ones Of Animals
5. Narmada River
The Narmada is known as the “Lifeline of Gujarat and Madhya Pradesh”. The river benefits both states. It is the largest one in Gujarat and the fifth largest one in the country.
The Narmada River is 1312 km long and originates from Amarkantak. The river flows in the westward direction, in contrast to the other rivers in India that flow in the east and drains into the Gulf of Khambhat in the Arabian Sea.
Its main tributaries are the Halon, Burhner, Barna, Heran, Dudhi, Shakkar, Banjar, Tawa, Kolar, Beda, Ganjal, Goi, and Orsang.
6. Indus River
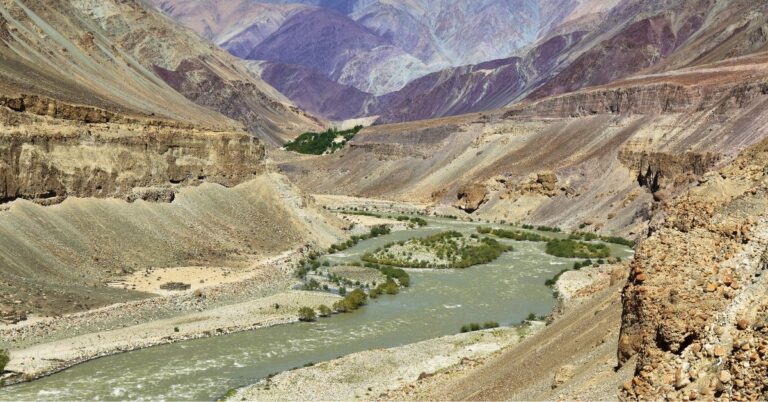

Indus River, (as a matter of fact the name India is derived from the Indus River) also known as ‘Sindhu River’ or ‘Puranik River’ is one of the longest rivers in India and has length of around 1114 km in India (total is 3180 km).
It is one of the most beautiful rivers in India. It originates from Mansarovar Lake in Tibet and falls to the Arabian Sea in Karachi, Pakistan.
The river is known to harbor one of the flourishing and oldest civilizations- the Indus Valley Civilization. The main tributaries of this river are Soan, Jansker, Chenab, Jhelum, Sutlej, Ravi, and Beas.
7. Brahmaputra River
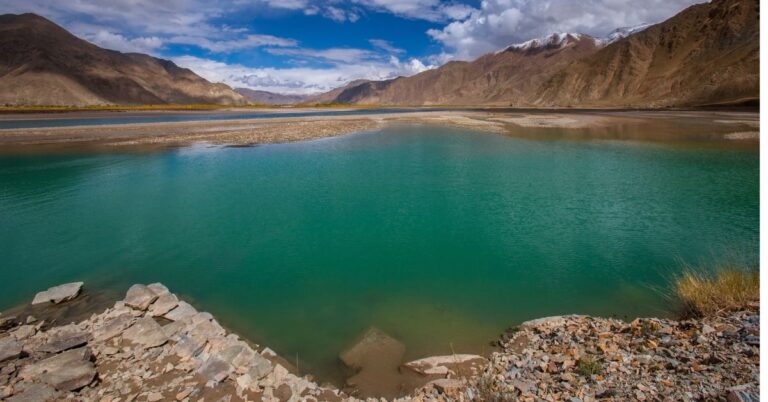

Brahmaputra has a male name. According to Hindu Mythology, the river Brahmaputra is considered to be the son of Lord Brahma, hence the name.
It is the ninth-largest in the world by discharge, originating from the Angsi glacier of the Kailash ranges of the Himalayas in Tibet and draining into the Bay of Bengal. The Brahmaputra enters in India through Arunachal Pradesh.
It originates from the Mansarover ranges and enters India through Arunachal Pradesh. While it is a 2900 km long river, its length in India is 916 kilometers.
Some of its main tributaries include Buroi, Ronganadi, Subansiri, and Dikrong on the North and Buridehing, Noadehing, Dikhow, Desang, and Bhogdoi, on the south.
Also Read: BREAKING THE CYCLE OF CHILDHOOD
8. Mahanadi River
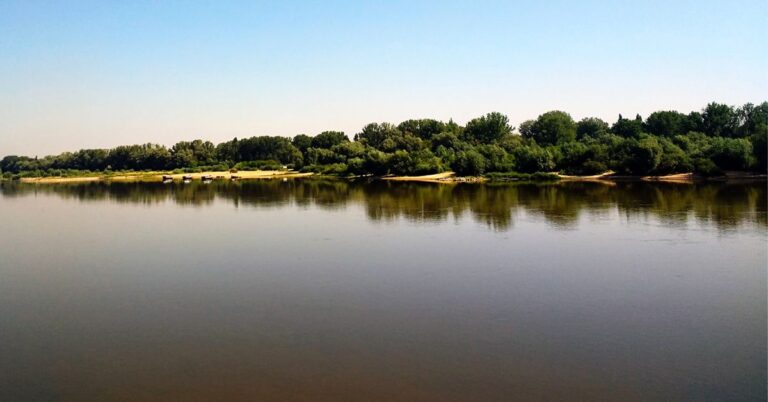

Mahanadi is one of the most famous rivers in East-Central India. It is a combination of many mountain streams. The river flows through the states of Odisha and Chhattisgarh.
The 900 km long river starts in the mountain streams of Eastern Ghats situated in the Dhamtari district of Chhattisgarh and ends in the Bay of Bengal. Its principal tributaries are Hasdeo, Mand, Parry river, Seonath, Ib, Ong, Telen, and Jonk.
9. Kaveri River

According to Hindu mythology, Kaveri is considered to be a holy and sacred river in South India. It is the third largest river after Krishna and Godavari.
Kaveri River originates at Talakaveri, located in the Kodagu district in Karnataka. It is 800 km long and outfalls into the Bay of Bengal. It is the 9th largest river in India. The numerous tributaries of the Kaveri River include Shimsha, Arkavathy, Hemavati, Kapil, Honnuhole, Amaravati, Bhavani, and Tirtha.
10. Tapti River

Tapti River is between the Narmada and Godavari rivers. It flows over a length of 724 km. It rises in the Satpura range in Multai, a holy place. The basin of this river lies mainly in the states of Gujarat, Maharashtra, and Madhya Pradesh. It flows from the eastern Satpura range in South Madhya Pradesh and drains to the Arabian Sea through the Gulf of Khambhat.
The tributaries of Tapti include Vaki, Aner, Arunawati, Gomai, Nesu, Amravati, Buray, Panjhara, Bori, Girna, Waghur, Purna, Mona, and Sipna. This river has a major extent of cultural and religious importance in the lives of Indian people.
11. Sutlej River
Sutlej River also known as Satluj or the Satadree is the longest of the five tributaries of the Indus and also the easternmost tributary of it. It runs through the famous crossroads area of the state of Punjab in North India and Pakistan.
The major portion of the river flows through the regions of Pakistan. The river is 1,450 km long and starts in the lake Rakshastal in Tibet. It ends in the Arabian Sea near the port city of Karachi, Pakistan.
It is a major source of hydroelectric power as it flows quickly. Several dams have been completed on the river. Sutlej is also famous for running at a very high altitude. The river is part of the Indus River system.
Also Read: 12 Ways to Prepare Your Child for a School Interview
12. Chambal River
Chambal River is one of the major tributaries of the river Yamuna. The river flows North East through Madhya Pradesh and reaches the Yamuna in the state of Uttar Pradesh. The river is 1,024 km long.
It rises from the Bhadakla Falls in Janapav Hills and meets Yamuna in the Etawah district of Uttar Pradesh. Chambal River has many tributaries, some of them are Shipra, Choti Kalisindh, Sivanna, Parbati, Seep, Kuwari, Kuno, Alnia, and Mej.
Conclusion
These are the longest and most popular rivers in India. These rivers are not only a great source of drinking water for us, but they also act as resources for agriculture, transportation, electricity, and more. These rivers have both cultural and economic importance in India.
Frequently Asked Questions
The Indus River is the longest river in India, with a distance of over 3000 kilometers. It originates from the Lake Mansarover and ends in the ocean southeast of Karachi.
The longest tributary of the Ganges is the Yamuna River. It starts from the Yamunotri glacier.